Definition of Expert systems are:
– Knowledge based systems
– Part of the Artificial Intelligence field
– Computer programs that contain some subject-specific knowledge of one or more human experts
– Made up of a set of rules that analyze user supplied information about a specific class of problems.
– Systems that utilize reasoning capabilities and draw conclusions.
Terms Associated with Expert Systems
+ Knowledge Engineering – building an expert system
+ Knowledge Engineers – the people who build the system
+ Knowledge Representation – the symbols used to represent the knowledge
+ Factual Knowledge – knowledge of a particular task domain that is widely shared
+ Heuristic Knowledge – more judgmental knowledge of performance in a task domain.
Uses of Expert Systems
– Very useful to companies with a high-level of experience and expertise that cannot easily be transferred to other members.
– Solves problems that would normally be tackled by a medical or other professional.
– Currently used in fields such as accounting, medicine, process control, financial service, production, and human resources
Prominent Expert Systems
> MYCIN – used to diagnose infectious blood diseases and recommend antibiotics.
> DENDRAL – embedded a chemist’s knowledge of mass spectrometry rules to use in analysis.
> CADUCEUS – used to analyze blood-borne infectious bacteria
> CLIPS and Prolog programming languages are both used in expert systems
– The Age of Empire game uses CLIPS to control its AI
Building an Expert System
+ Can be built from scratch – using lots of if-then-else statements.
+ There are many products being sold to make programming these systems easier.
A few that I’m aware of:
– Exsys – http://www.exsys.com – provides an easy to use user interface to develop traditional applications or web-based solutions.
– Barisoft – http://www.barisoft.com – developed by a PSU professor and finely tuned by his students
– CLIPS – provides a complete environment for the construction of rules and/or object based expert systems
– Jess – the Rule Engine, built
Components of an Expert System
> Set of Rules – derived from the knowledge base and used by the interpreter to evaluate the inputted data
> Knowledge Engineer – decides how to represent the experts knowledge and how to build the inference engine appropriately for the domain
> Interpreter – interprets the inputted data and draws a conclusion based on the users responses.
Problem-solving Models
+ Forward-chaining – starts from a set of conditions and moves towards some conclusion
+ Backward-chaining – starts with a list of goals and the works backwards to see if there is any data that will allow it to conclude any of these goals.
+ Both problem-solving methods are built into inference engines or inference procedures
Knowledge Objects
– Classes – questions the user is asked
– Parameters – place holder for a character string which can be variable and used to decide if/when a question is asked
– Procedures – definitions of calls to external procedures
– Rule Nodes – inferencing is done by a tree structure (decision trees!) and the nodes are called rule nodes.
Advantages of Expert Systems
+ Provide consistent answers for repetitive decisions, processes and tasks.
+ Hold and maintain significant levels of information.
+ Reduce employee training costs
+ Centralize the decision making process.
+ Create efficiencies and reduce the time needed to solve problems.
+ Combine multiple human expert intelligences
+ Reduce the amount of human errors.
+ Give strategic and comparative advantages creating entry barriers to competitors
+ Review transactions that human experts may overlook.
Disadvantages of Expert Systems
> Lack human common sense needed in some decision making.
> Will not be able to give the creative responses that human experts can give in unusual circumstances.
> Domain experts cannot always clearly explain their logic and reasoning.
> Challenges of automating complex processes.
> Lack of flexibility and ability to adapt to changing environments.
> Not being able to recognize when no answer is available.
References :
– “Expert Systems and Artificial Intelligence”. Engelmore, R., Feigenbaum, E., Chapter 1. http://www.wtec.org/loyola/kb/c1_s1.htm
– “The Origin of Rule-Based Systems in AI”, Davis, R., King, J.
– “Expert System – Wikipedia”, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Expert_system
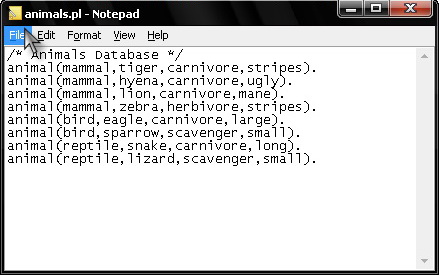
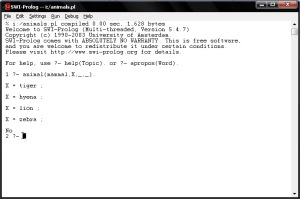
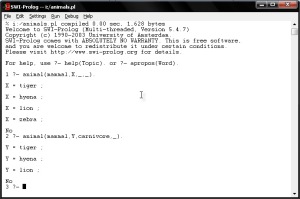
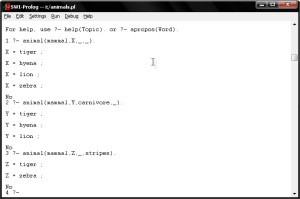
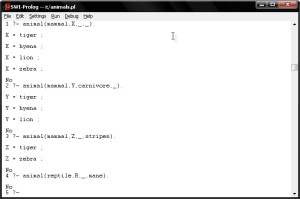
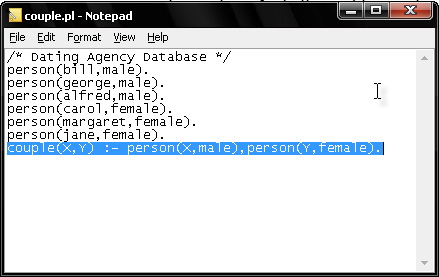 4. Consult your saved file in PROLOG.
4. Consult your saved file in PROLOG.